1. Lee HJ, Im SH, Kang SM. Implications for innovation in higher education from Minerva schools. Journal of Lifelong Learning Society. 2019;15(2):59-84. https://doi.org/10.26857/ jlls.2019.5.15.2.59

2. Chang MO, Jung MY. The study of awareness and preparation of college students for the era of 4th industrial revolution. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 2019;19(6):47-57. https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2019.19.06.047
3. Han SM. The relationships between the academic motivation variables cognitive strategies and academic achievement. The Korean Journal of Educational Psychology. 2004.18(1):329-350.
4. Yokoyama S. Academic self-efficacy and academic performance in online learning:A mini review. Frontiers in Psychology. 2019;9, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02794

5. Kweon YR, Choi BS. Effects of a psychiatric nursing education using flipped learning on learning transfer motivation and learning self-efficiency of nursing college students. Journal of The Korean Data Analysis Society. 2020;22(1):447-460. https://doi.org/10.37727/jkdas.2020.22.1.447

6. Kim NI, Chun BA, Choi JI. A case study of flipped learning at college:Focused on effects of motivation and self-efficacy. Journal of Educational Technology. 2014;30(3):467-492. https://doi.org/10.17232/KSET.30.3.467

7. Son EJ, Park JH, Im IC, Lim Y, Hong SW. Impact of flipped learning applied at a class on learning motivation of collage students. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement and Intervention. 2015.6(2):97-117.
8. Jung HK, Lee SH. The effects of flipped learning method on a college student's self directed learning ability critical thinking disposition learning motivation, and learning satisfaction. Journal of Korean Academy of Dental Technology. 2017.39(3):171-177.
9. Jeong HH. A study of loyalty to flipped learning applied at college courses-the relationship among learning motivation learning engagement satisfaction, and loyalty. Journal of Educational Technology. 2017;33(3):537-565. https://doi.org/ 10.17232/kset.33.3.537

10. Do SJ, Jin YS. The effect of flipped learning on ETP TOEIC class. Korean Journal of General Education. 2018.12(2):149-167.
11. Hong KC. Effects of flipped learning on self-directed learning ability and learning motivation of college students. The Journal of Thinking Development. 2016.12(4):41-61.
12. Kim SY. Flipped learning operation and effect analysis of scientific literacy enhancement education program in college setting [master's thesis]. Seoul: Dankook University; 2018. p. 1-81.
13. Gweon HS. A study on effectiveness of flipped learning in social welfare education. Journal of Korean Social Welfare Administration. 2018.20(3):39-72.
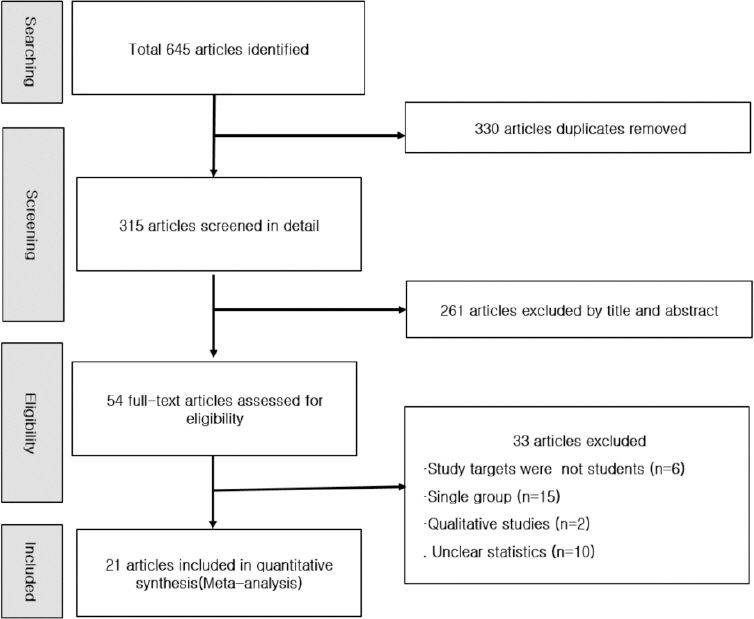
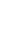
14. Hwang SD. Publication bias in meta-analysis:Its meaning and analysis. The Korean Journal of the Human Development. 2016;23(1):1-19. https://doi.org/10.15284/kjhd. 2016.23.1.1

15. Suh MO. The meta analysis of the effectiveness of flipped classroom. Journal of Educational Technology. 2016;32(4):707-741. https://doi.org/10.17232/kset.32.4.707

16. Yoon SH. A meta-analysis for effects of flipped learning on secondary school students. Journal of Education &Culture. 2018;24(2):459-476. https://doi.org/10.24159/joec.2018.24.2.459

17. Cho BR, Lee JM. Meta-analysis of flipped learning design characteristics. Korean Journal of Teacher Education. 2018;34(2):1-21. https://doi.org/10.14333/kjte.2018.34.2.1

18. Lee HJ, Ahn MS, Lee JG. A meta-analysis of the effects of flipped learning and team-based learning in college classes. Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction. 2018;18(21):1253-1280. http://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2018.18.21.1253

19. Kang HJ, Cho DY. A delphi study on human resource development policy directions and tasks for the 4th industrial revolution. The Korean Journal of Human Resource Development Quarterly. 2017.19(4):1-34.

20. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell; 2011. p. 321-374.
21. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. West Sussex, UK: John Wiley &Sons, Ltd; 2009.
22. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988. p. 19-74.
24. Joo SY. A meta-analysis of web-based problem-based learning program. Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction. 2018;18(20):105-124. http://doi.org/10.22251/ jlcci.2018.18.20.105

25. In: Bergmann J, Sams A, editors. Flip your classroom:Reach every student in every class every day. United states of America: International Society for Technology in Education; 2012. p. 1-123.
26. Han SM. A study on learning driving force of flipped learning for learner centered education. Journal of Practical Engineering Education. 2020;12(2):293-299. http://doi%.org/10. 14702/JPEE.2020.293
27. Go JS, Kwon KJ, Kim YG, Won YJ. Development of a futuristic class model for moral leadership training-sungkyun in dream. Confucianism Culture Research. 2014.58, 177-204.
28. Nam CM, Shin DM. The effects of blended learning instructional strategies and flipped-learning instructional strategies on undergraduate students'social presence and group cohesion. The Korean Society for Creative Information Culture. 2019;5(1):1-13. http://www.doi.org/10.32823/jcic.5. 1.201904.1
29. Kim HY, Kim YH. An action research on flipped learning for fundamental nursing practice courses. Journal of Korean Academy Fundamentals Nursing. 2017;24(4):265-276. https://doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2017.24.4.265

30. Ozdamli F, Asiksoy G. Flipped classroom approach. World Journal on Educational Technology:Current Issues. 2016;8(2):98-105. https://doi.org/10.18844/wjet.v8i2.640